SAF-sustainable aviation fuel
Sustainable Aviation Fuel
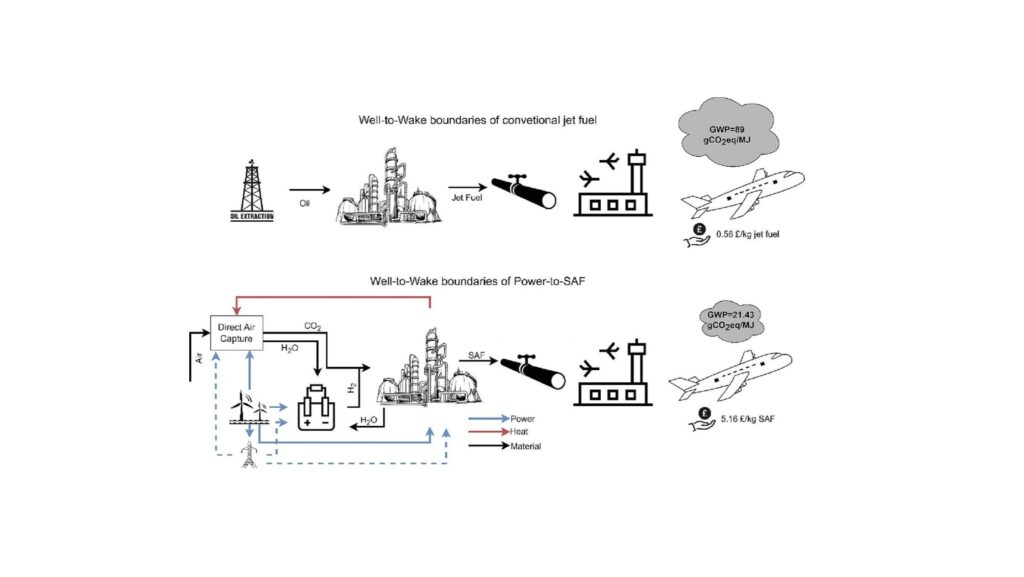
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is an alternative fuel made from non-petroleum feedstocks that reduces emissions from air transportation. SAF can be blended at different levels with limits between 10% and 50%, depending on the feedstock and how the fuel is produced. According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), over 360,000 commercial flights have used SAF at 46 different airports largely concentrated in the United States and Europe.
Worldwide, aviation accounts for 2% of all carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and 12% of all CO2 emissions from transportation. ICAO’s Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) caps net CO2 aviation emissions at 2020 levels through 2035. The international aviation industry has set an aspirational goal to reach net zero carbon by 2050. SAF presents the best near-term opportunity to meet these goals. The Sustainable Aviation Fuel Grand Challenge, announced in 2021, brings together multiple federal agencies for the purpose of expanding domestic consumption to 3 billion gallons in 2030 and 35 billion gallons in 2050 while achieving at least a 50% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits
Renewable hydrocarbon biofuels offer many benefits, including:
Engine and infrastructure compatibility—SAF blended with conventional Jet A can be used in existing aircraft and infrastructure.
Fewer emissions—Compared with conventional jet fuel, 100% SAF has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 94% depending on feedstock and technology pathway.
More flexibility—SAF is a replacement for conventional jet fuel, allowing for multiple products from various feedstocks and production technologies.
Compatibility
SAF can be used in existing aircraft and infrastructure without modifications, making it a "drop-in" fuel.
Global Adoption
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) has set goals for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, with SAF playing a key role.
Economic Potential
SAF offers opportunities for green job creation and fostering innovation in renewable energy and waste management sectors.
Environmental Benefits:
Reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by up to 80% compared to traditional fossil jet fuel over the fuel's lifecycle.
Production
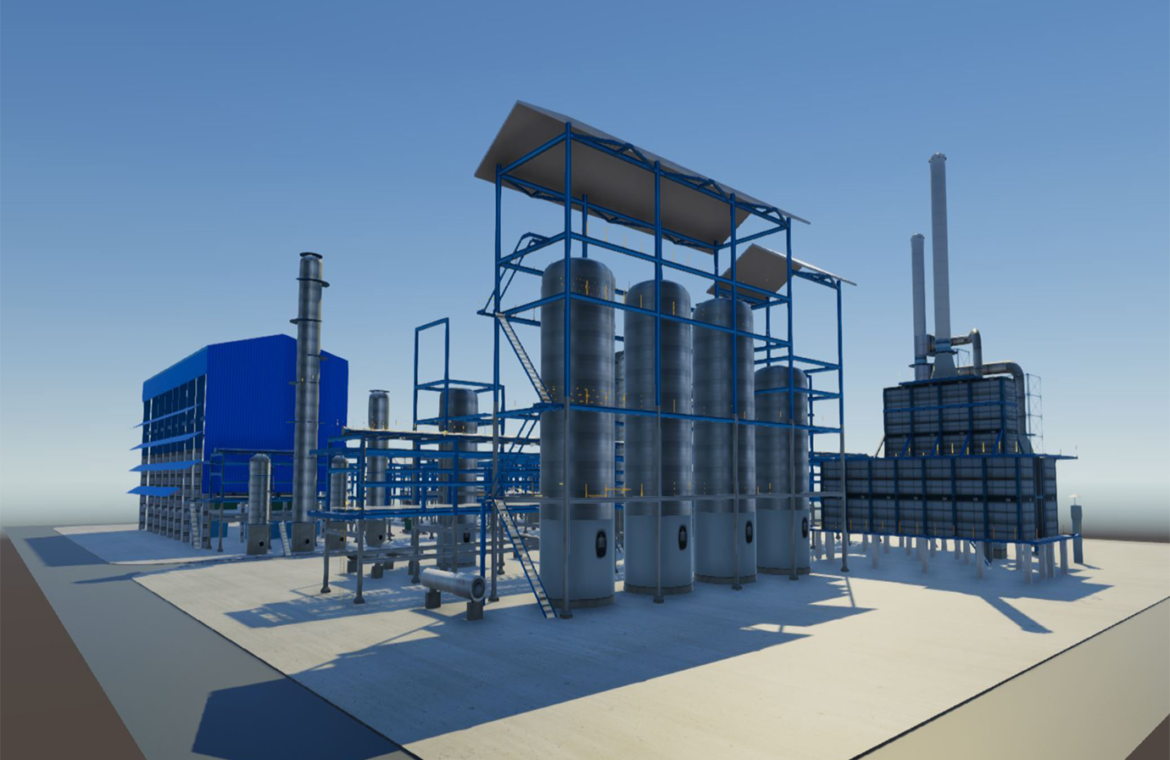
SAF can be produced from non-petroleum-based renewable feedstocks including, but not limited to, the food and yard waste portion of municipal solid waste, woody biomass, fats/greases/oils, and other feedstocks. SAF production is in its early stages, with three known commercial producers:
- World Energy began SAF production in 2016 at its Paramount, California, facility and initially supplied fuel to Los Angeles International Airport prior to supplying additional California airports.
- International producer Neste began supplying SAF to San Francisco International Airport in 2020 before expanding to other California airports in 2021 and 2022, as well as Aspen/Pitkin County Airport and Telluride Regional Airport, both in Colorado.
- Montana Renewables LLC began production in partnership with Shell at an existing petroleum production plant in 2023, supplying fuel to several partner airlines.